Six African powers that rivaled Rome and Persia
The African continent has an extraordinary history but its past is often overshadowed by the ancient kingdoms and enormous empires of the Mediterranean and Middle East. But did you know African societies were just as rich and complex?
From the very beginning of the continent's recorded history all the way up to the colonial period, Africa was home to a variety of important and powerful kingdoms and empires that few people know about today. Here’s a list of six important ones.
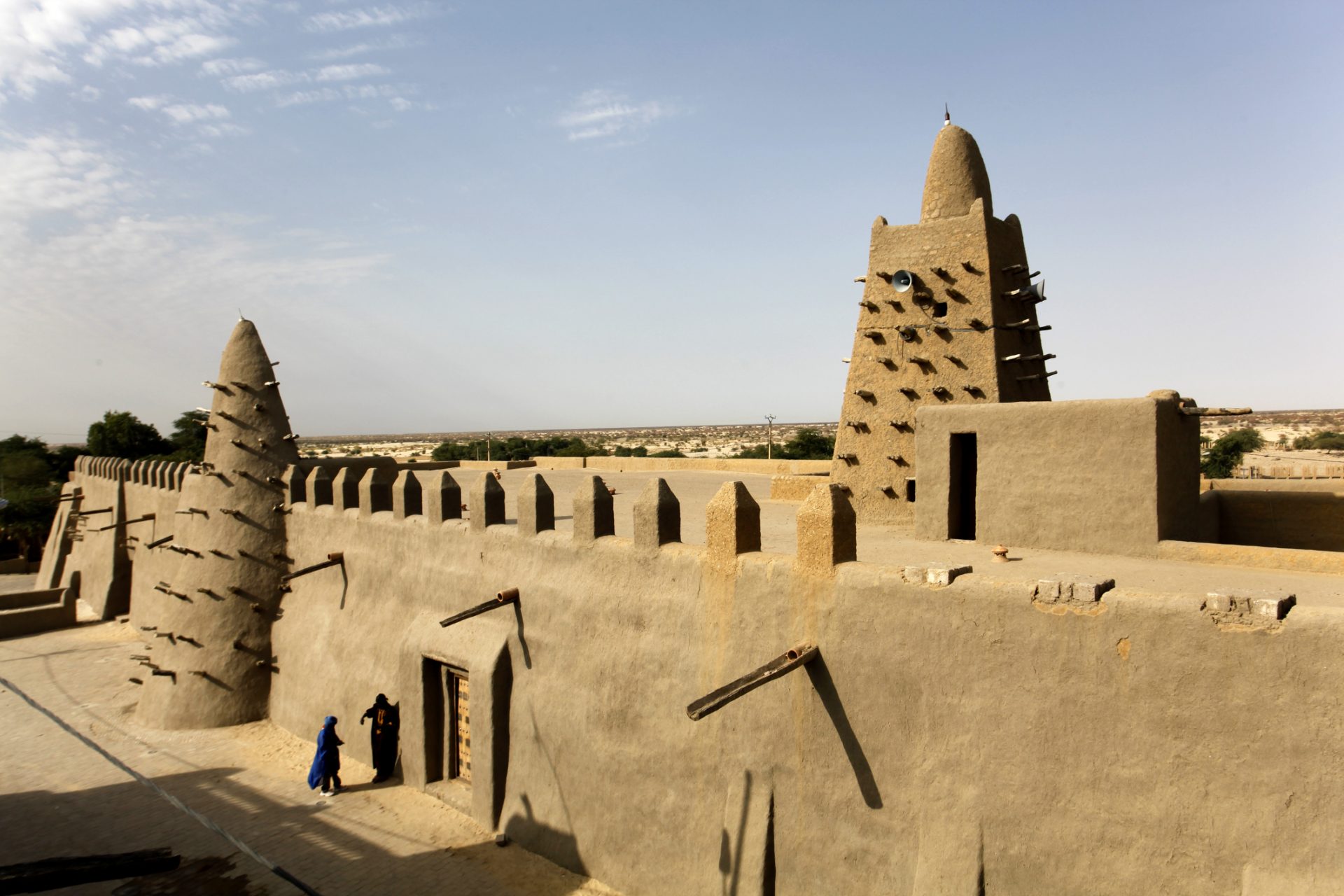
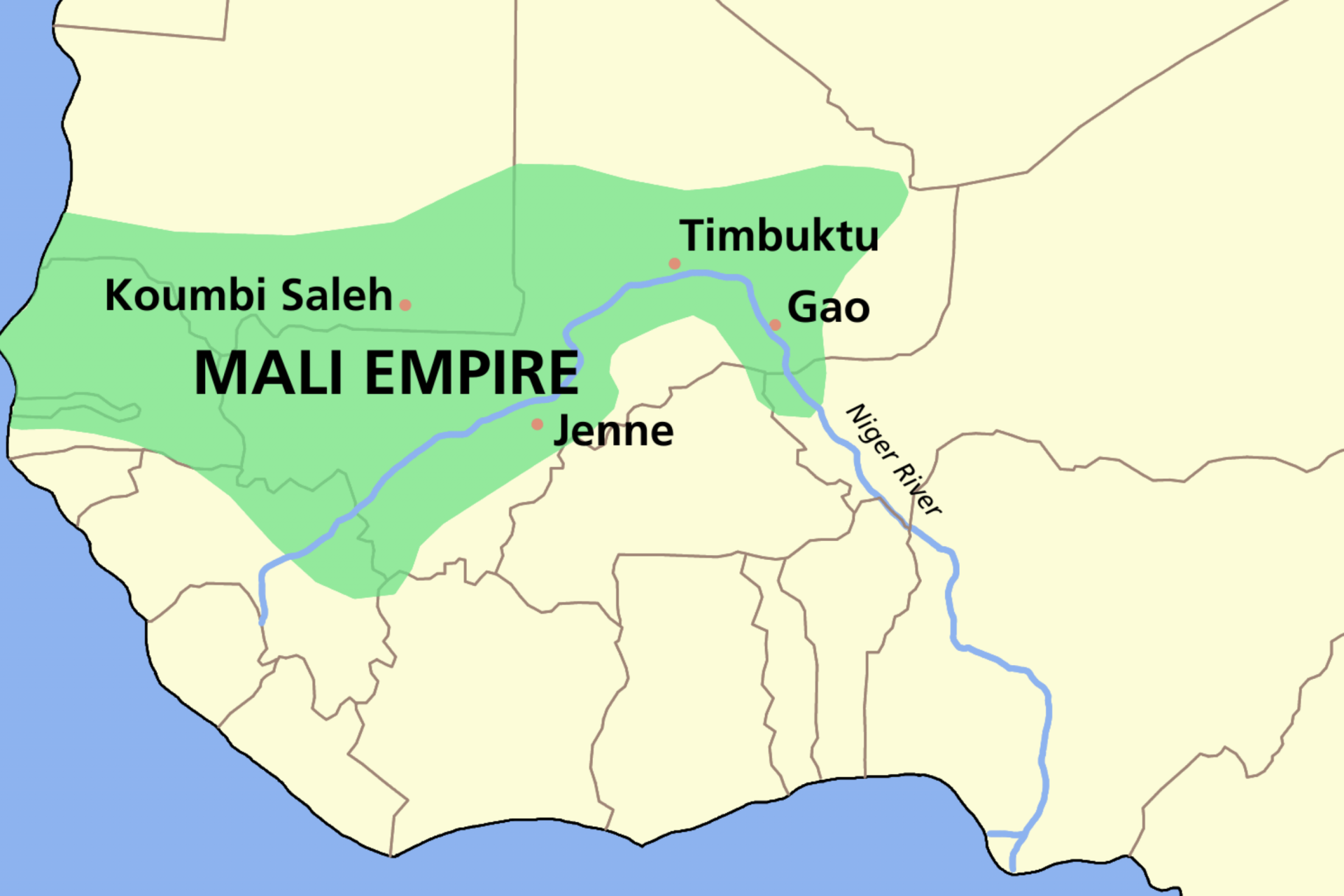
The Mali Empire was established in Western Africa in 1235 CE when a confederation of powers overthrew the region's previous rulers, the Sosso Empire. Mali reached its zenith in the 14th century and ruled over four hundred cities in Africa.
CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=552646
Live Science pointed out that only the Mongol Empire and Inca Empire were larger than the Mali Empire during this time period, which shows just how powerful the empire was at a time when European nations were nowhere near as large.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons CC BY-SA 3.0
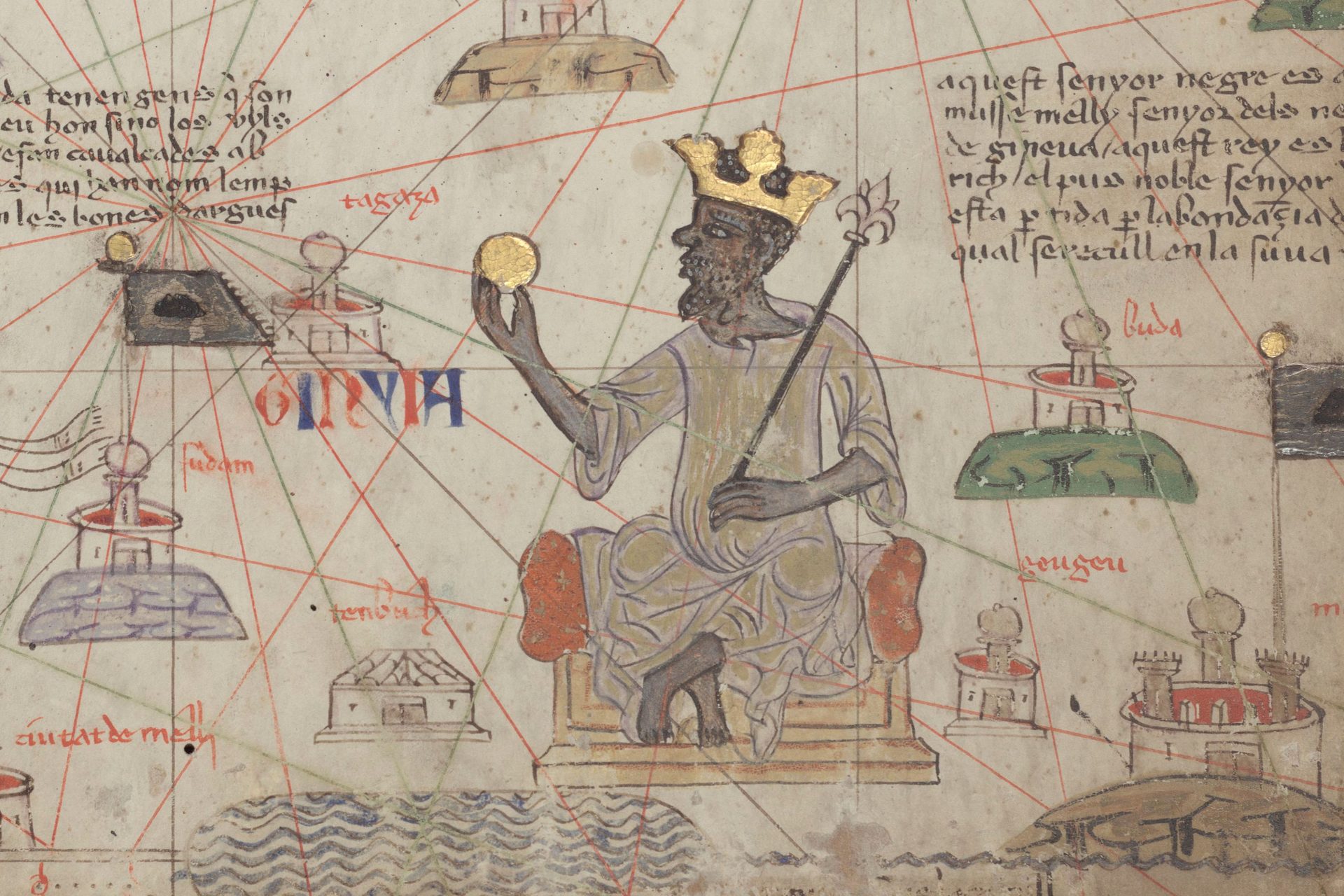
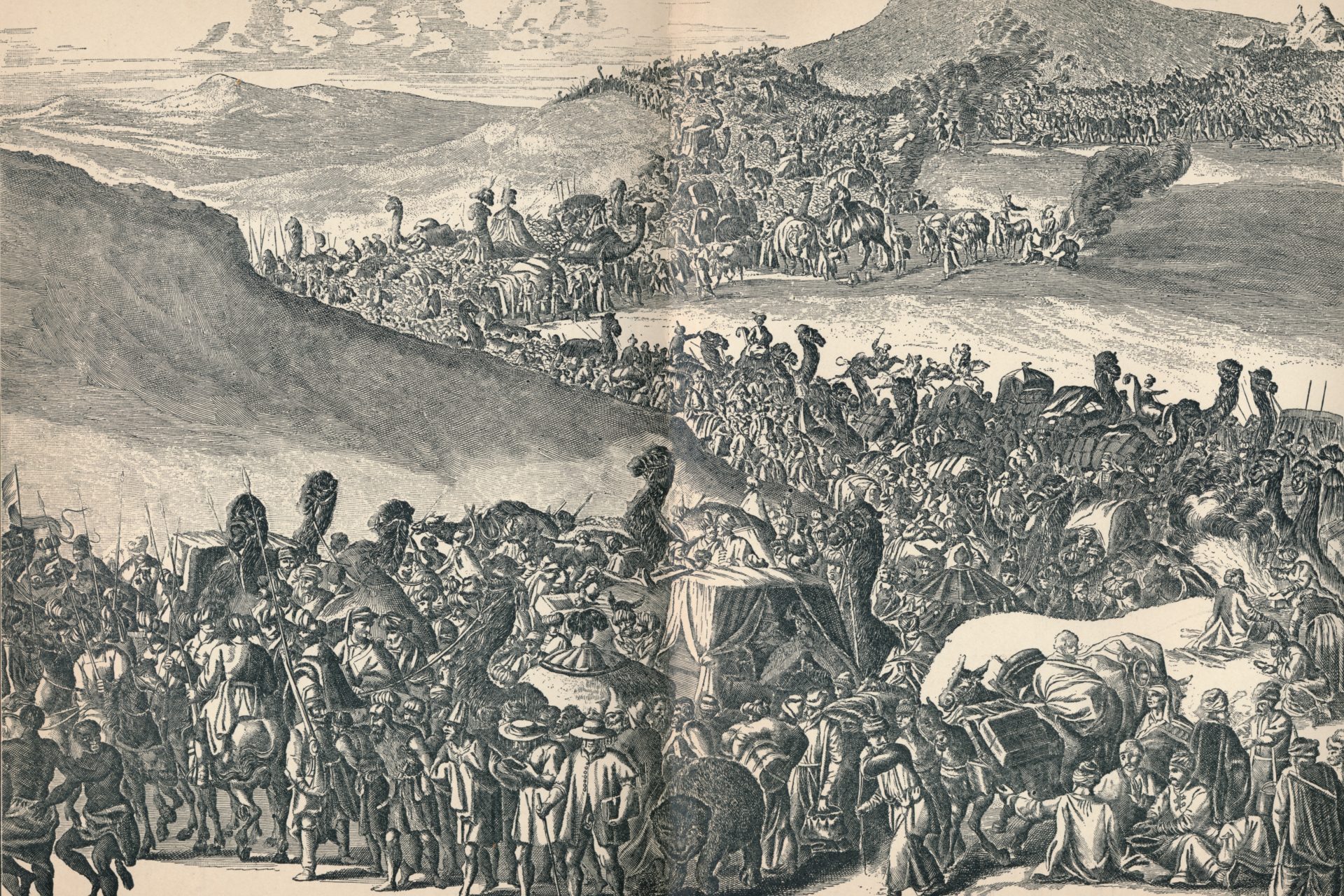
One revealing anecdote about the wealth and power of the Mali Empire at its peak can be found in the story of its ninth ruler Mansa Musa. Musa went on a pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324 CE and gave away so much gold he decreased its value.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Abraham Cresques / Gallica Digital Library
National Geographic noted that this story may have only related to gold values in Egypt but did mention that Arab intellectuals at the time wrote about Musa’s caravans of gold. Legends of Musa’s wealth eventually made their way to Europe.
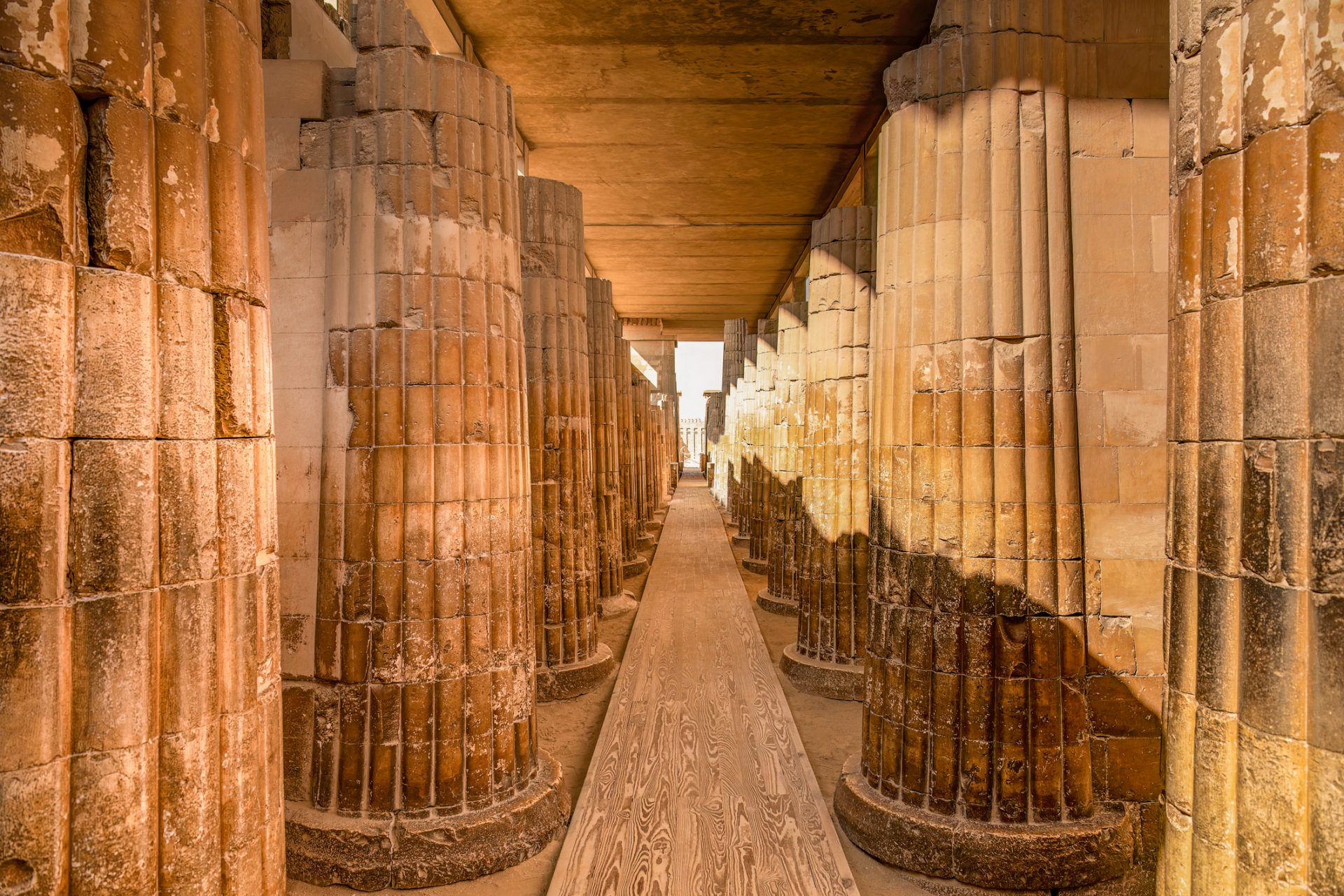
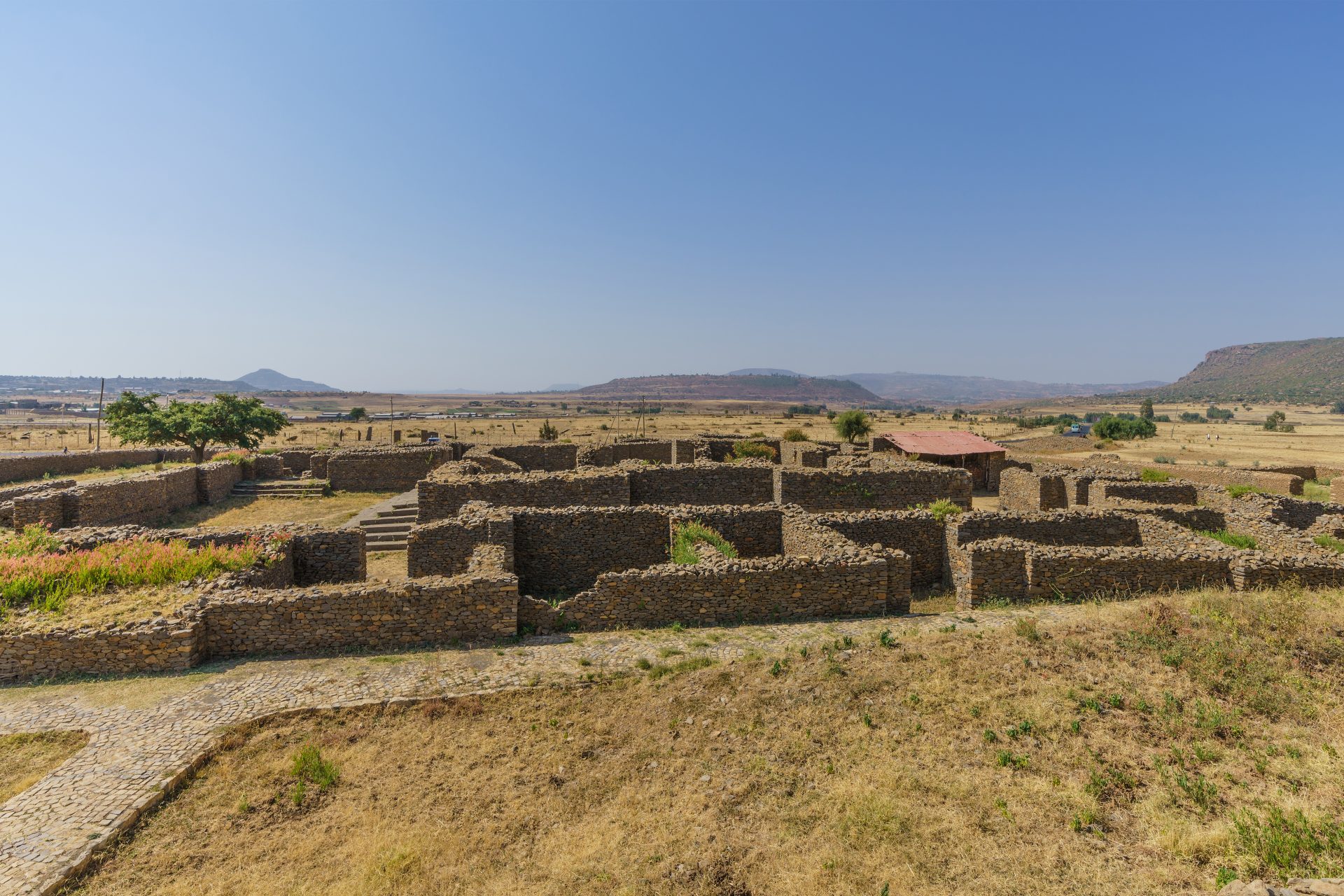
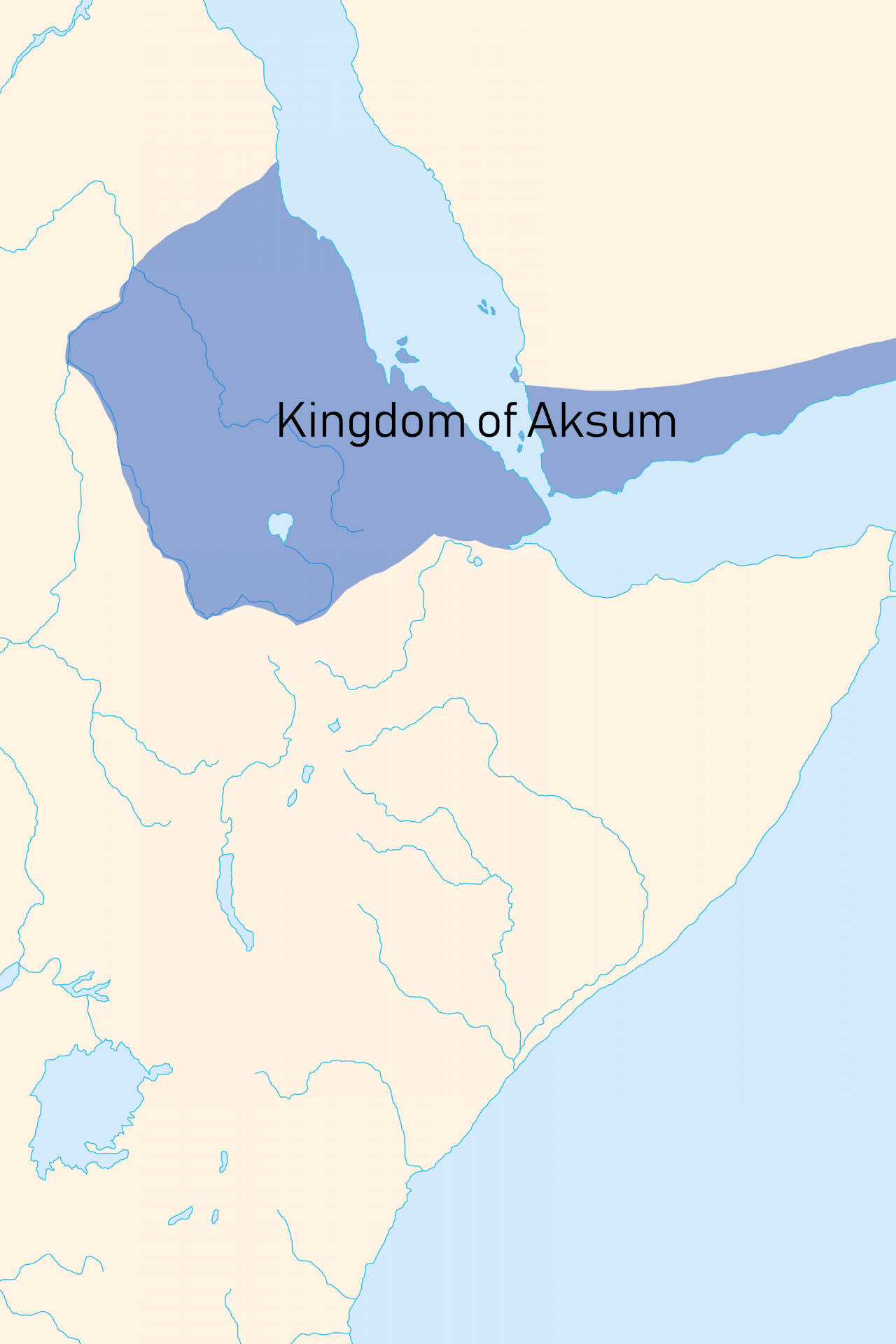
Most people have never heard of the Kingdom of Aksum but Live Science explained that it was one of the most powerful kingdoms of the ancient world. Located on the Red Sea, it was a hub of Africa’s ivory, gold, and spice trade with Rome.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Aldan-2 - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0
The Kingdom of Aksum had a prehistory that dated back to well before the Romans hit the scene and traces of their pre-culture can be dated to roughly 1600 BCE. However, Aksum reached its height of power in the 4th and 5th centuries.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By A.Savin - Own work, FAL
Research shows that Aksum was a big trading power between the 1st and 7th centuries and the peoples of this society developed their own writing system and body of literature at some point in the 4th century before converting to Christianity.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Sailko - Own work, CC BY 3.0
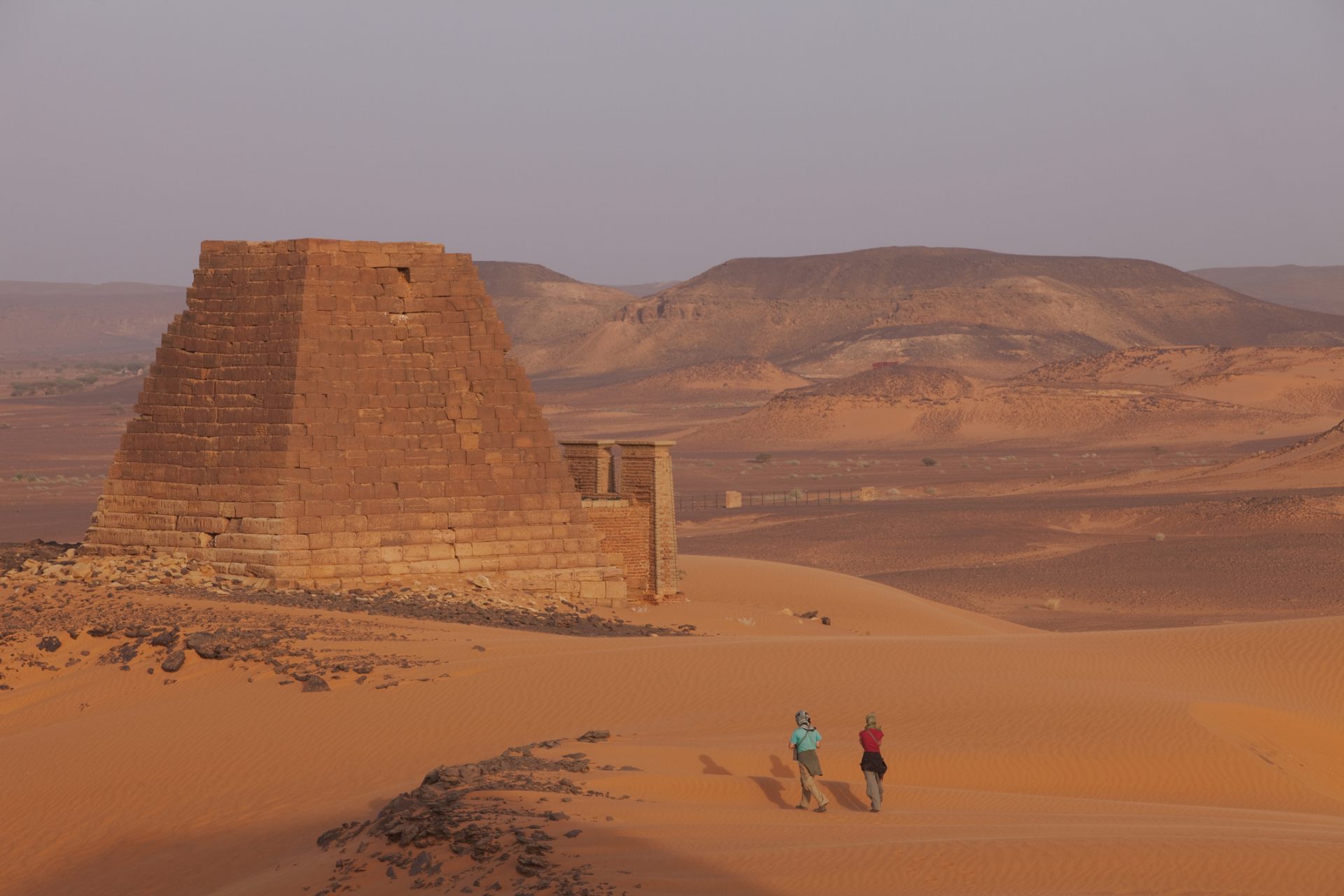
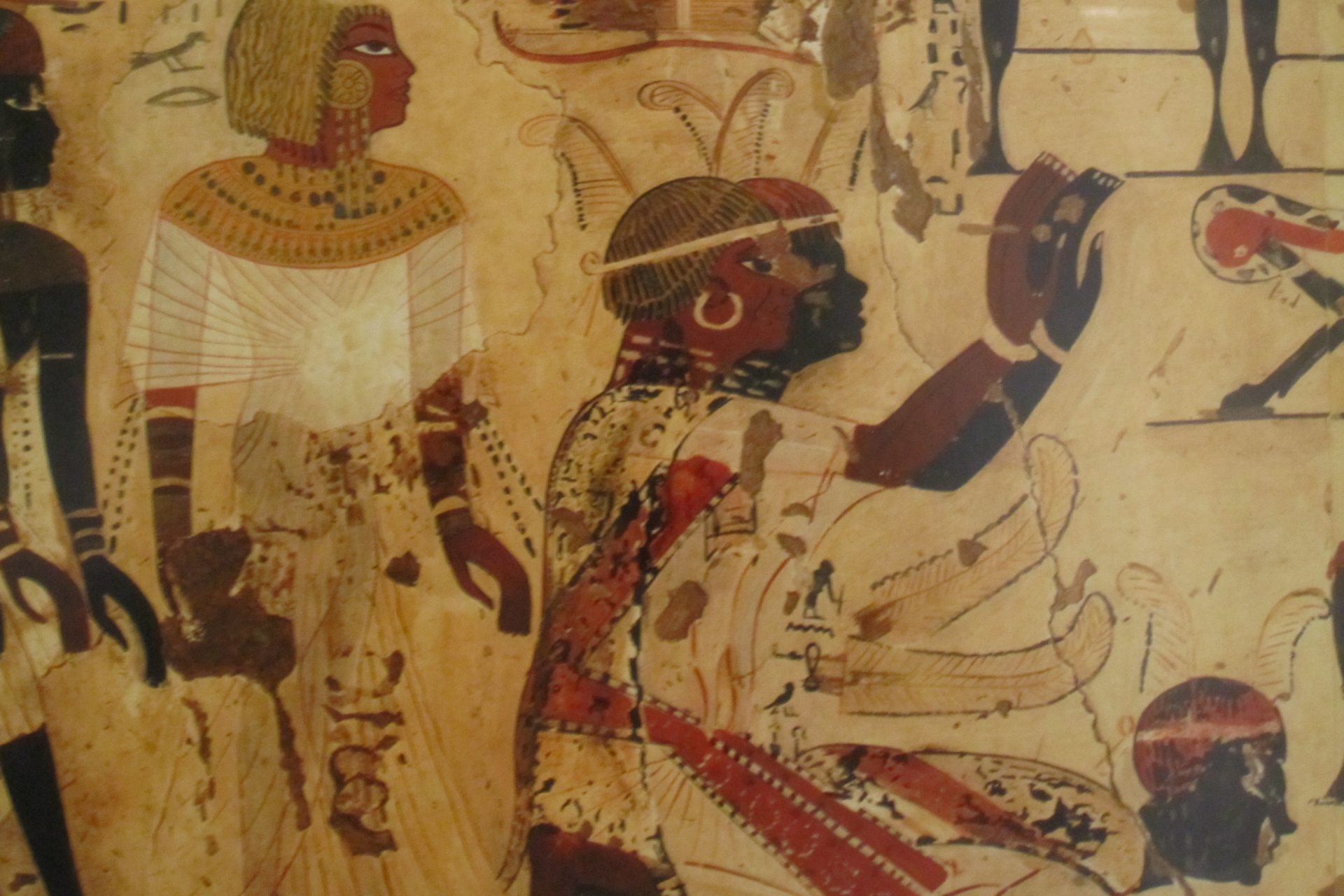
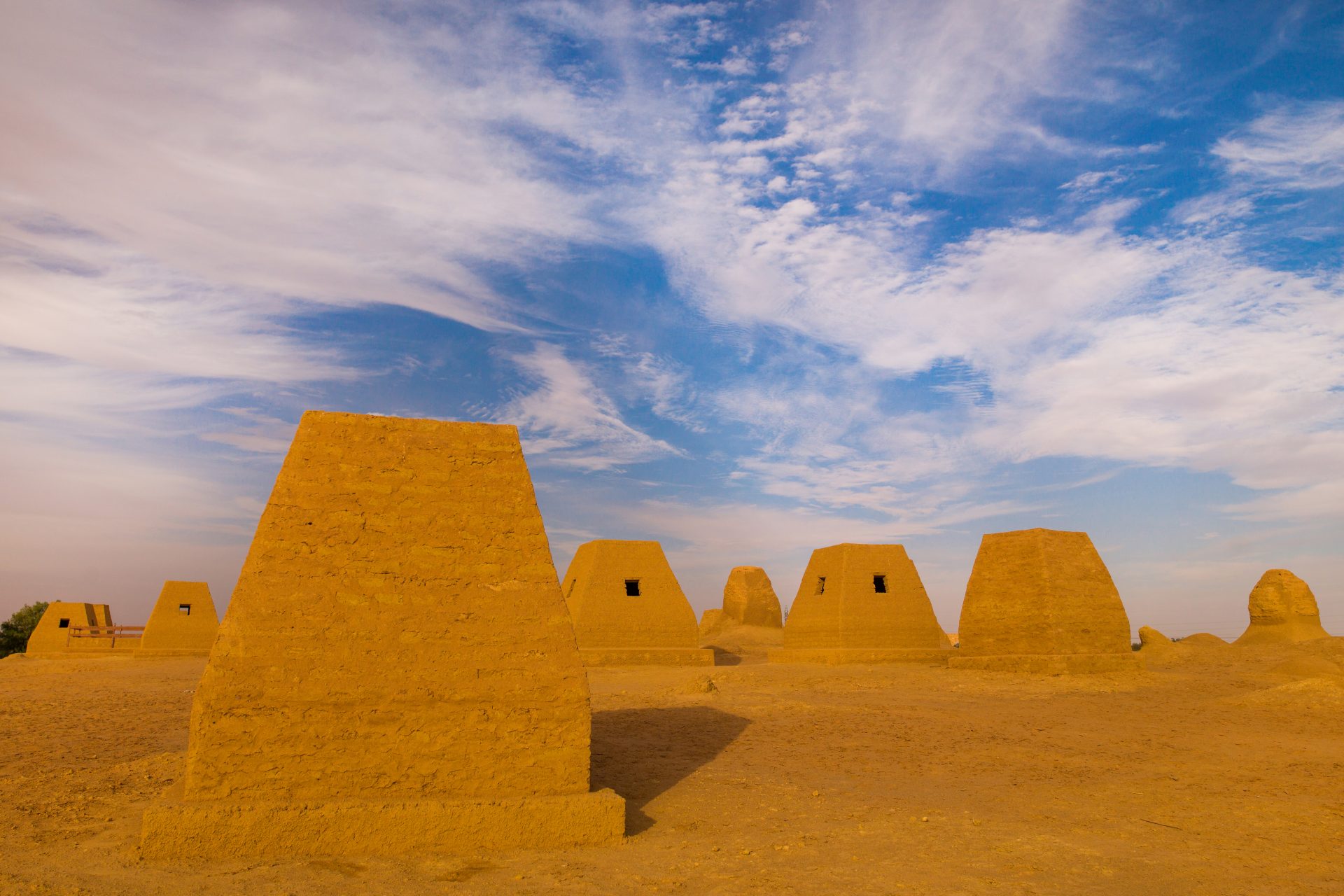
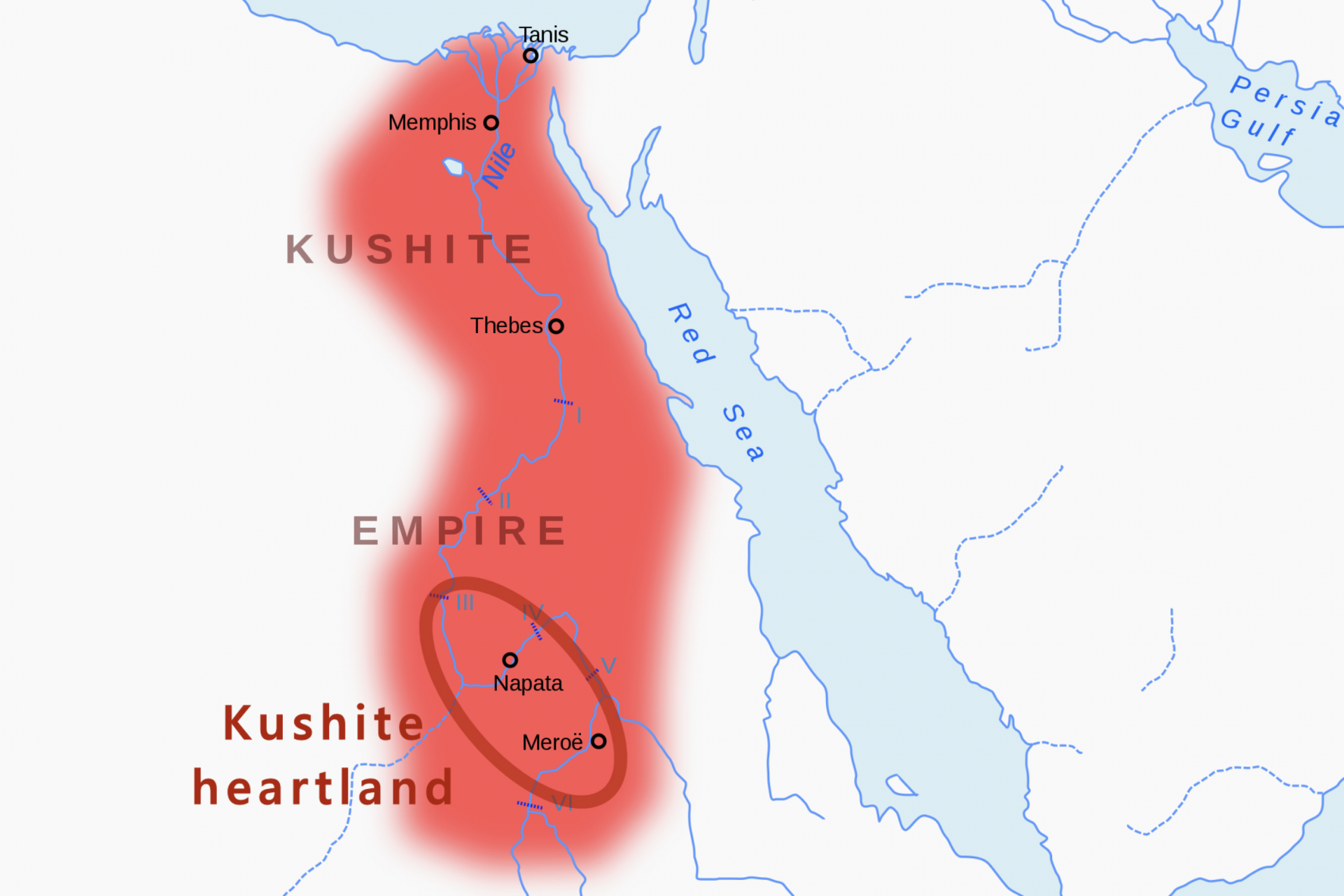
Kush is one of the few African kingdoms that most people might know about due to its centuries-long conflict with ancient Egypt. Located along the Nile in an area that was called Nubia at the time, the Kushites were ruled by Egypt until 1070 BCE.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons / Original map: Lommes Addition of Kushite heartland पाटलिपुत्र Source: National Geographic 2019 - CC BY-SA 4.0,
After the Kushites established their own independent kingdom, they became a powerful player in the region and even conquered Egypt between 712 to 664 BCE and ruled the ancient kingdom as its 25th Dynasty before its eventual decline.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By EditorfromMars - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0
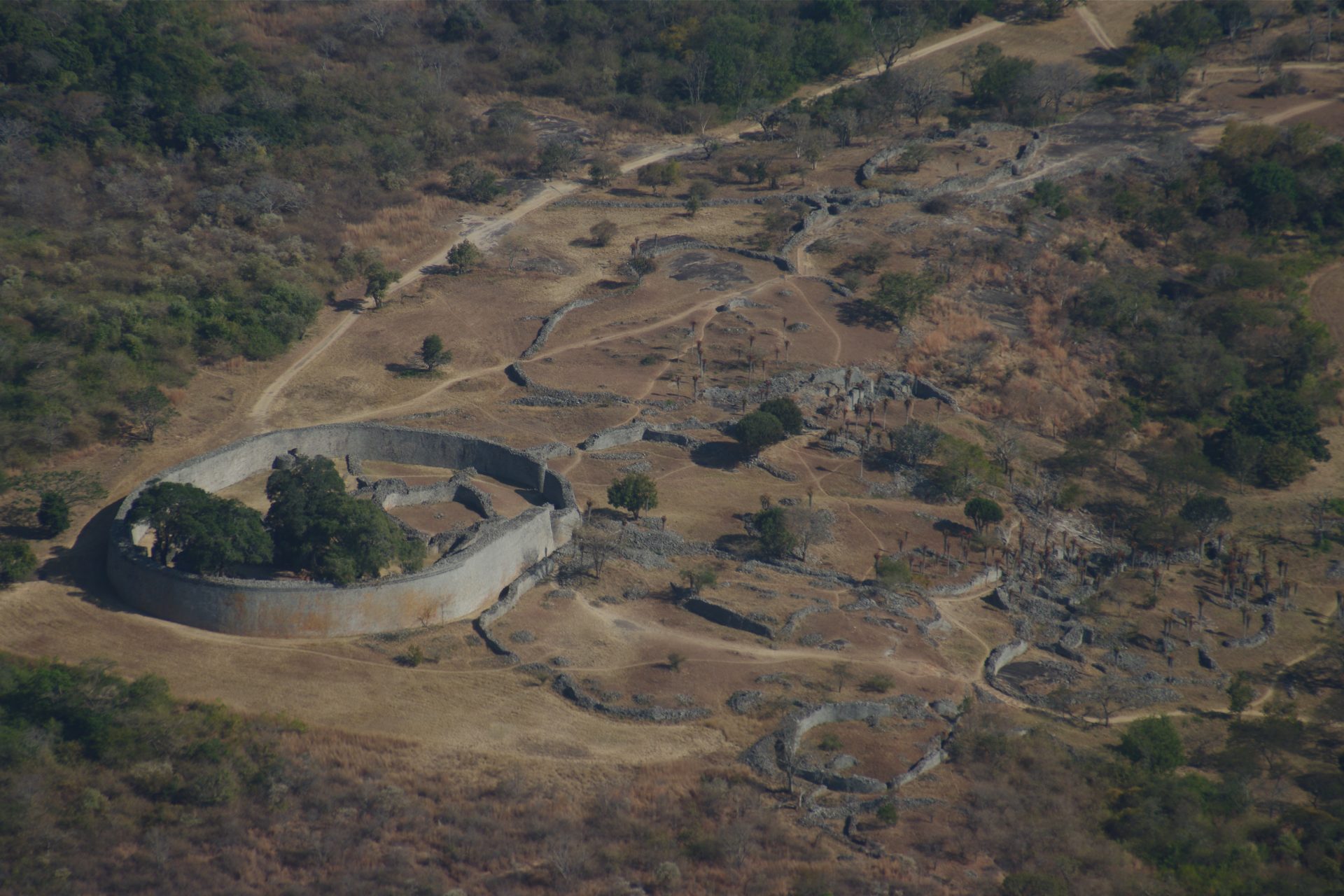
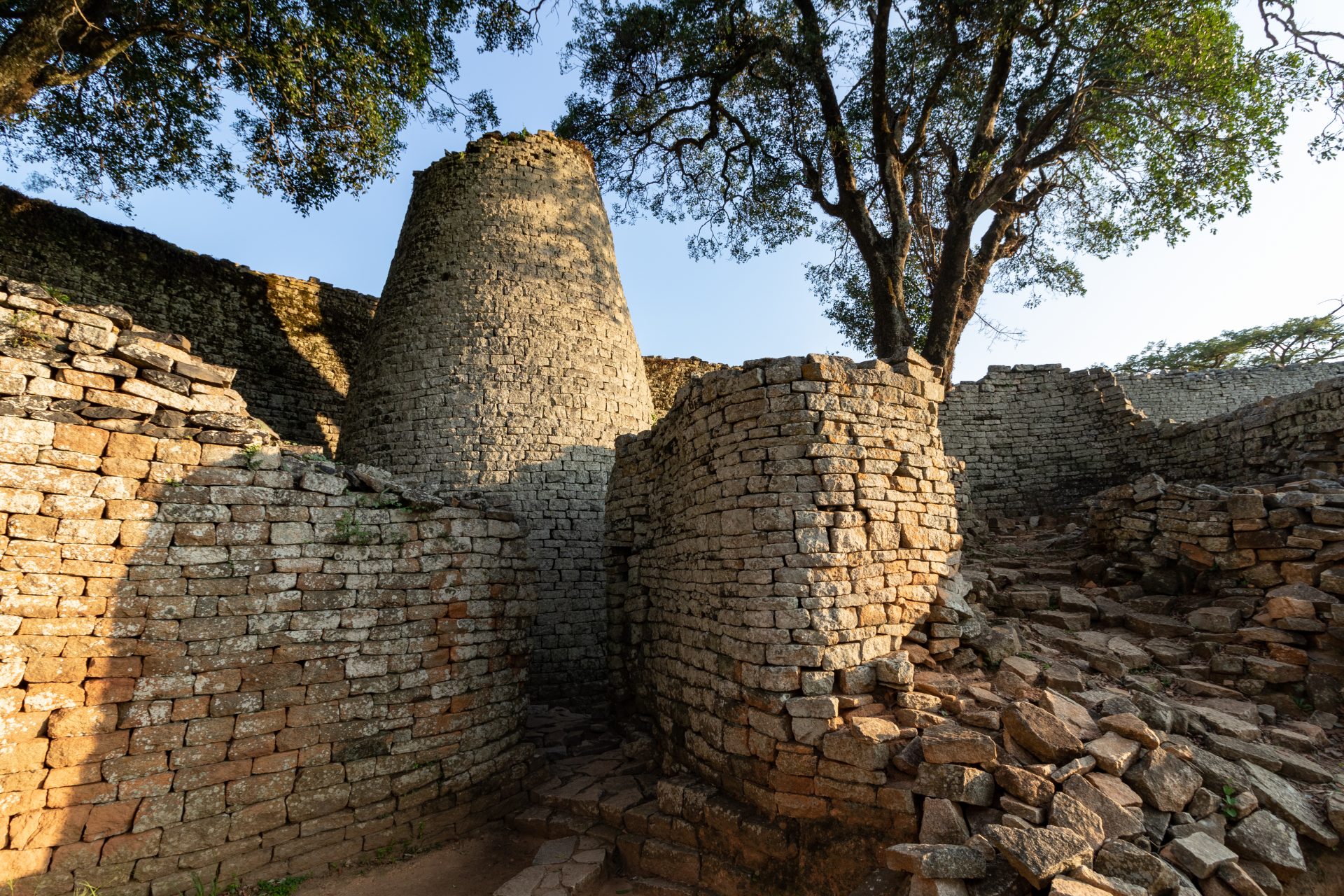
The Shona peoples of central southern Africa founded the Kingdom of Zimbabwe in the 13th century and little was known about it outside of the ruins of its capital city according to Live Science. However, we’ve learned a lot from the kingdom’s ruins.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Janice Bell - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0
Great Zimbabwe, the city’s name, was made from stones and mortar and was Africa’s largest pre-colonial stone structure in the south of the continent. The city could probably house as many as 18,000 people and had an intricate water collection system.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Andrew Moore from Johannesburg
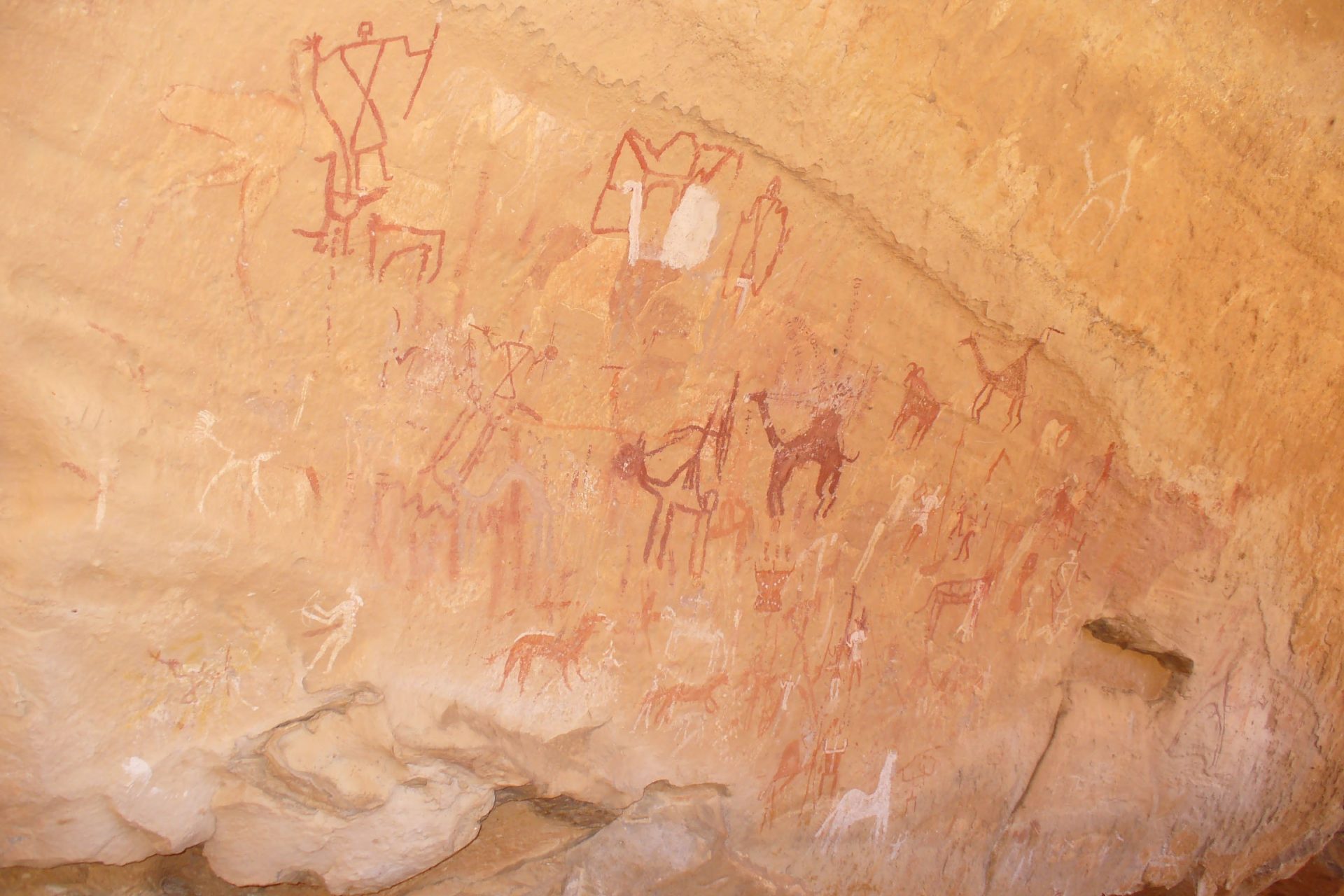
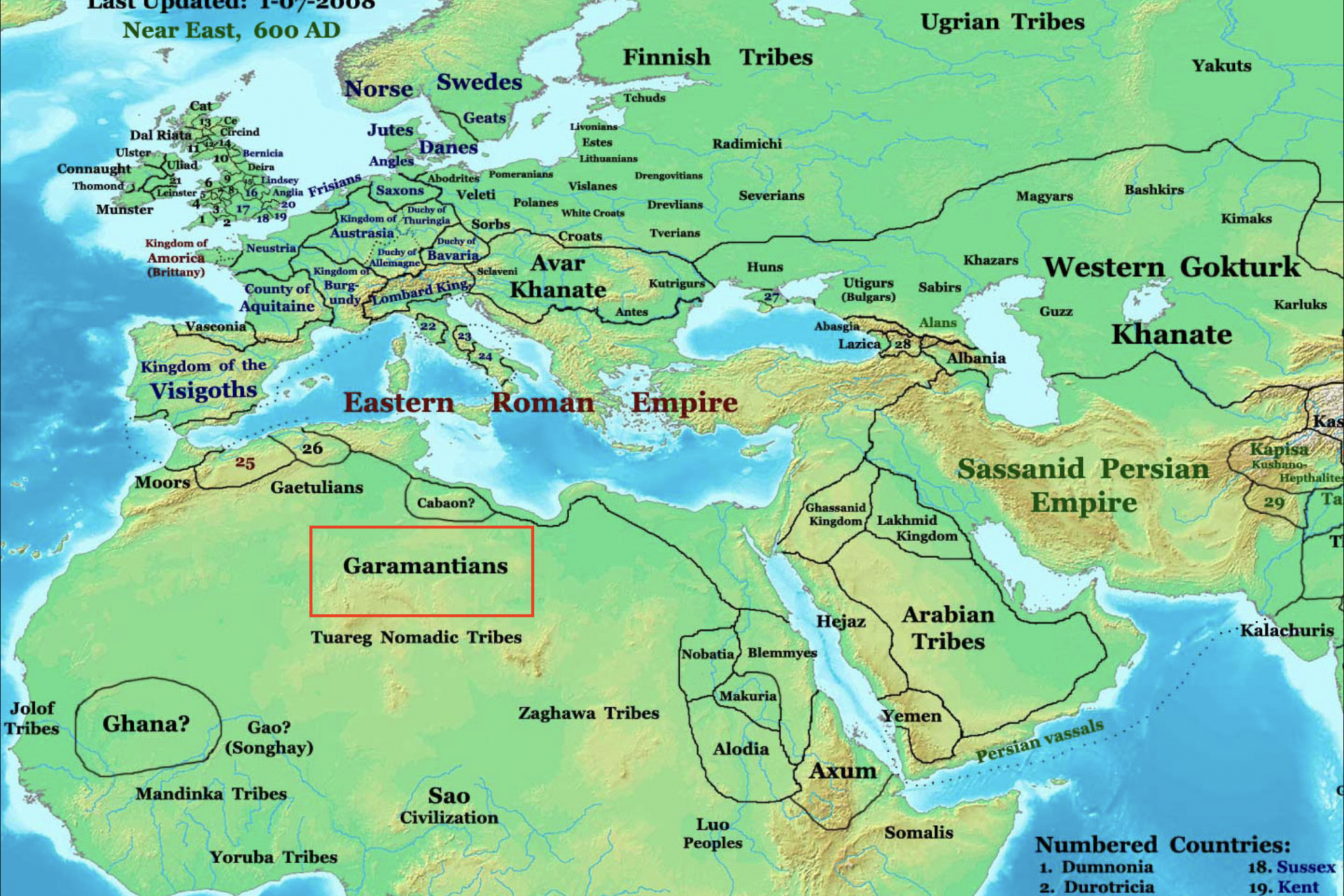
The Kingdom of the Garamantes was one of the major ancient groups in Northern Africa and it thrived in the Fezzan region of what is modern-day Libya. Decades of study have revealed a complex society that was home to several large cities.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Talessman at English Wikipedia
The Garamantes developed a very complicated system of irrigation known as foggaras that allowed them to transport water from ancient aquifers so that they could grow crops in the harsh desert environment that they called home.
“The Garamantes were also a powerful military force, with a well-trained army equipped with chariots, horses, and camels that the Garamantes used to expand their territory and protect their trade routes,” wrote Live Science’s Tom Metcalfe.
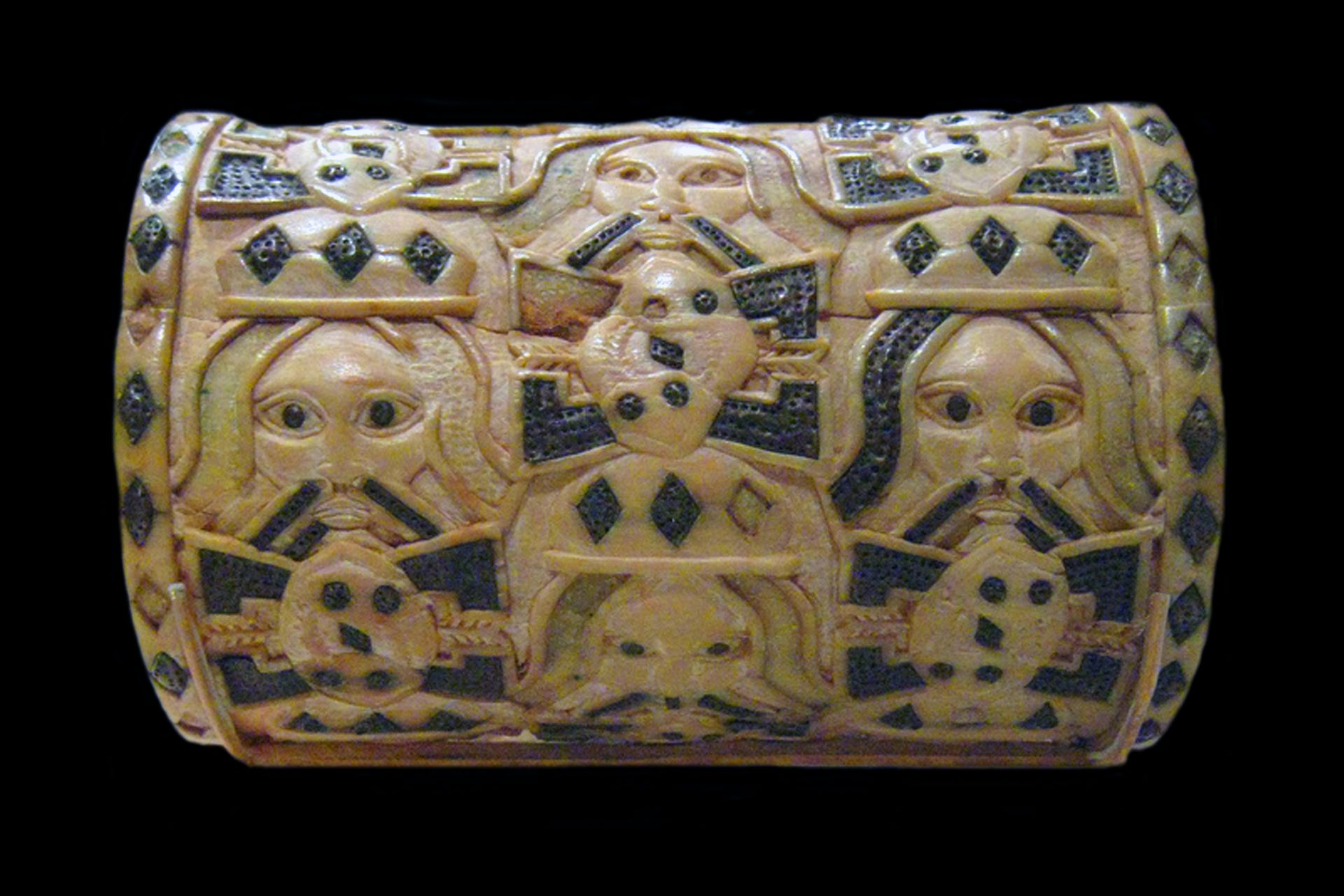
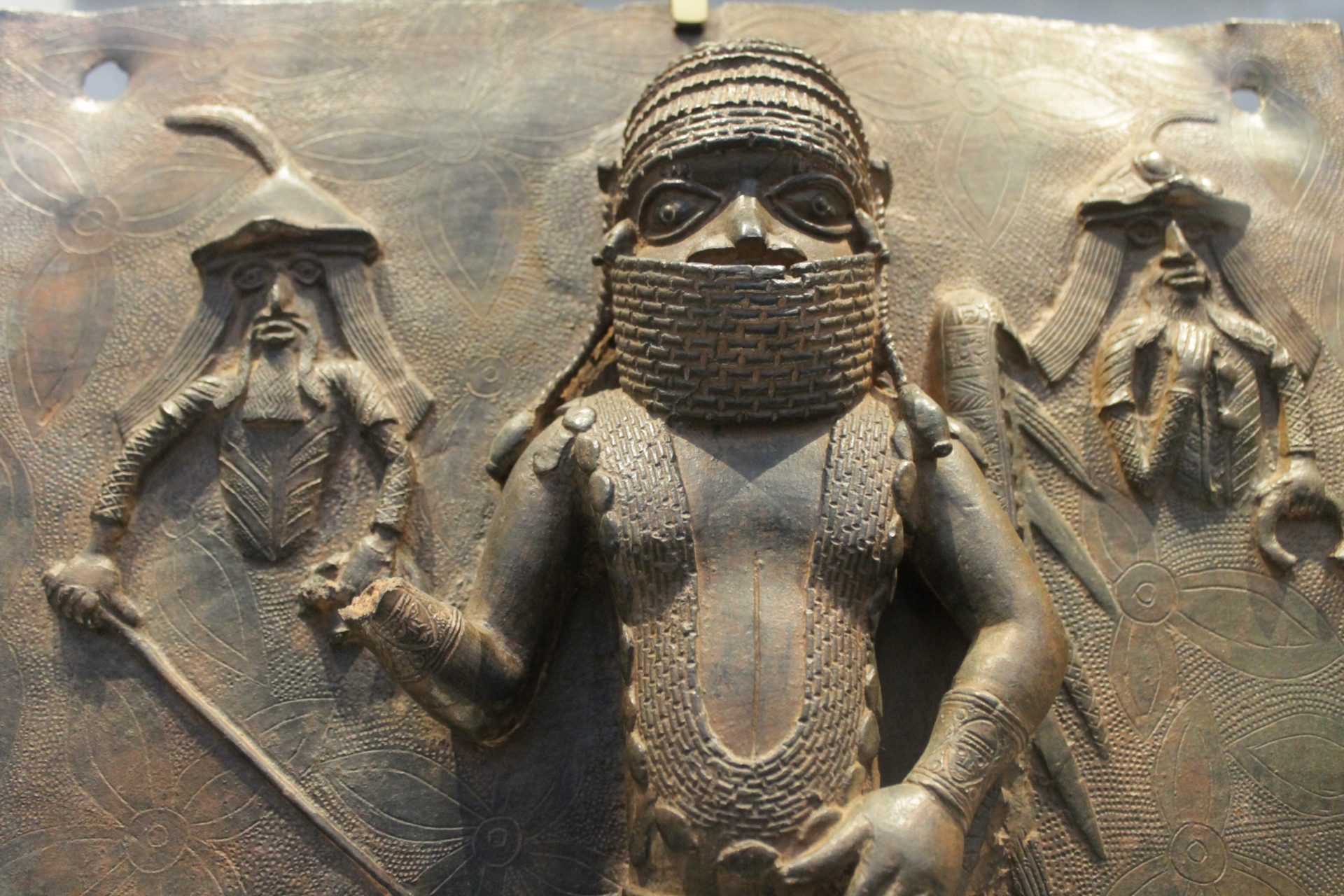
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as the Edo Kingdom, was the great power in Africa from the 12th century to the 19th century. It was the center of both trade and learning, which eventually came to prosper with the advent of the colonial slave trade.
National Geographic noted that trade was the lifeblood of the Benin Kingdom. Benin was rich in gold, ivory, and pepper, and its later trade connections with the Portuguese helped the kingdom remain a powerhouse of the continent.
“The kingdom reached its greatest power and size under Oba Ewuare the Great. He expanded the kingdom and improved the capital, present-day Benin City; the city was defined by massive walls,” wrote National Geographic.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Stephencdickson - Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0
More for you
Top Stories