Meet the ACS3: a new NASA project that could revolutionize space travel
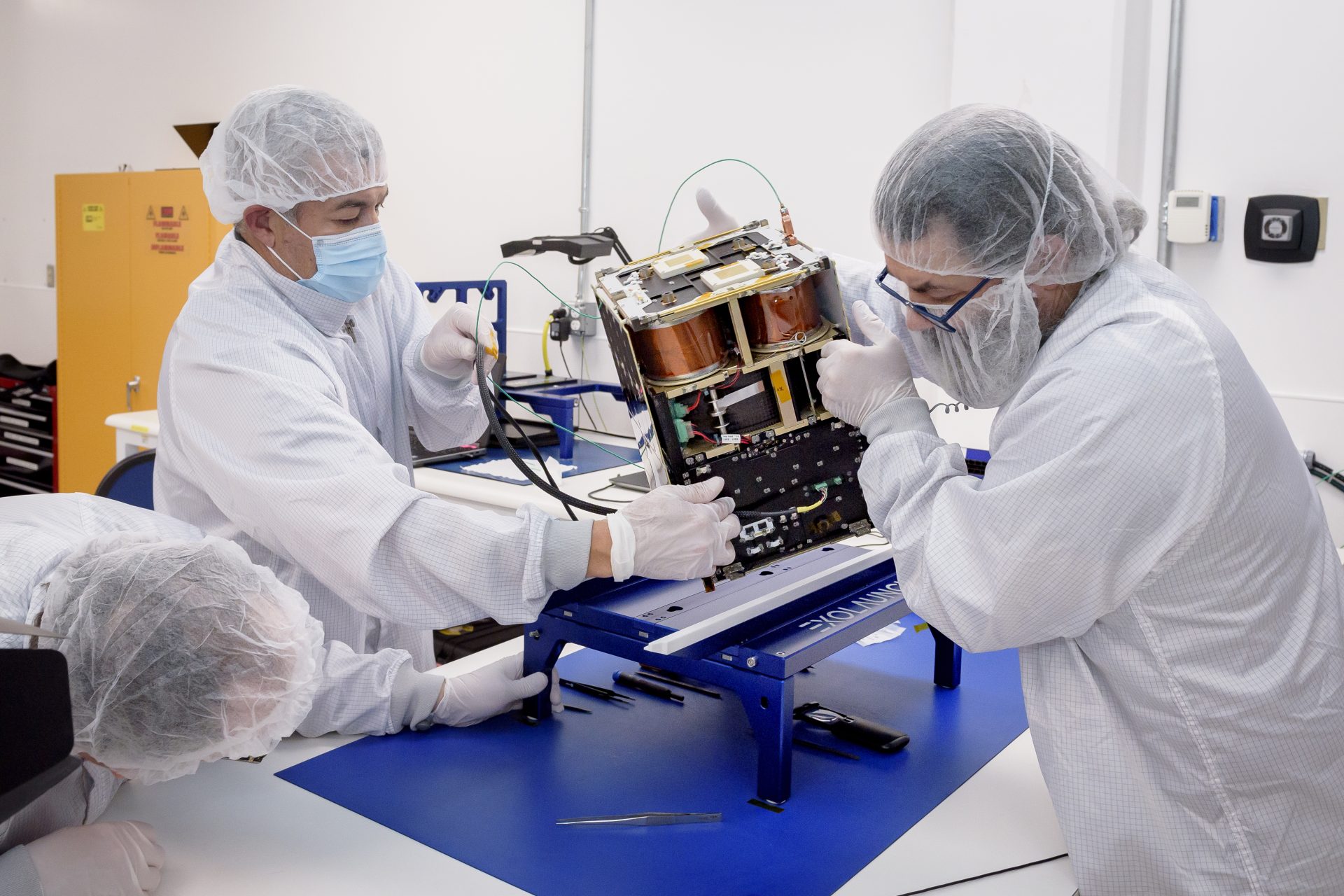
In April 2024, NASA launched a new project into space that was designed to test the limits of the agency's latest solar sail technology. The development was a major step forward that could revolutionize space travel forever.
If humans are ever going to become a spacefaring species then we need to figure out a few more efficient ways to traverse the cosmos. That’s why NASA developed its latest futuristic solar sail tech, which has raised eyebrows throughout 2024.
Solar sails may seem more science fiction than reality, but just four months after a new NASA solar sail project hitched a ride into space, it spread out its sails and proved that the concept could be a viable option for space travel.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By NASA/Marshall Space Flight Center, Public Domain
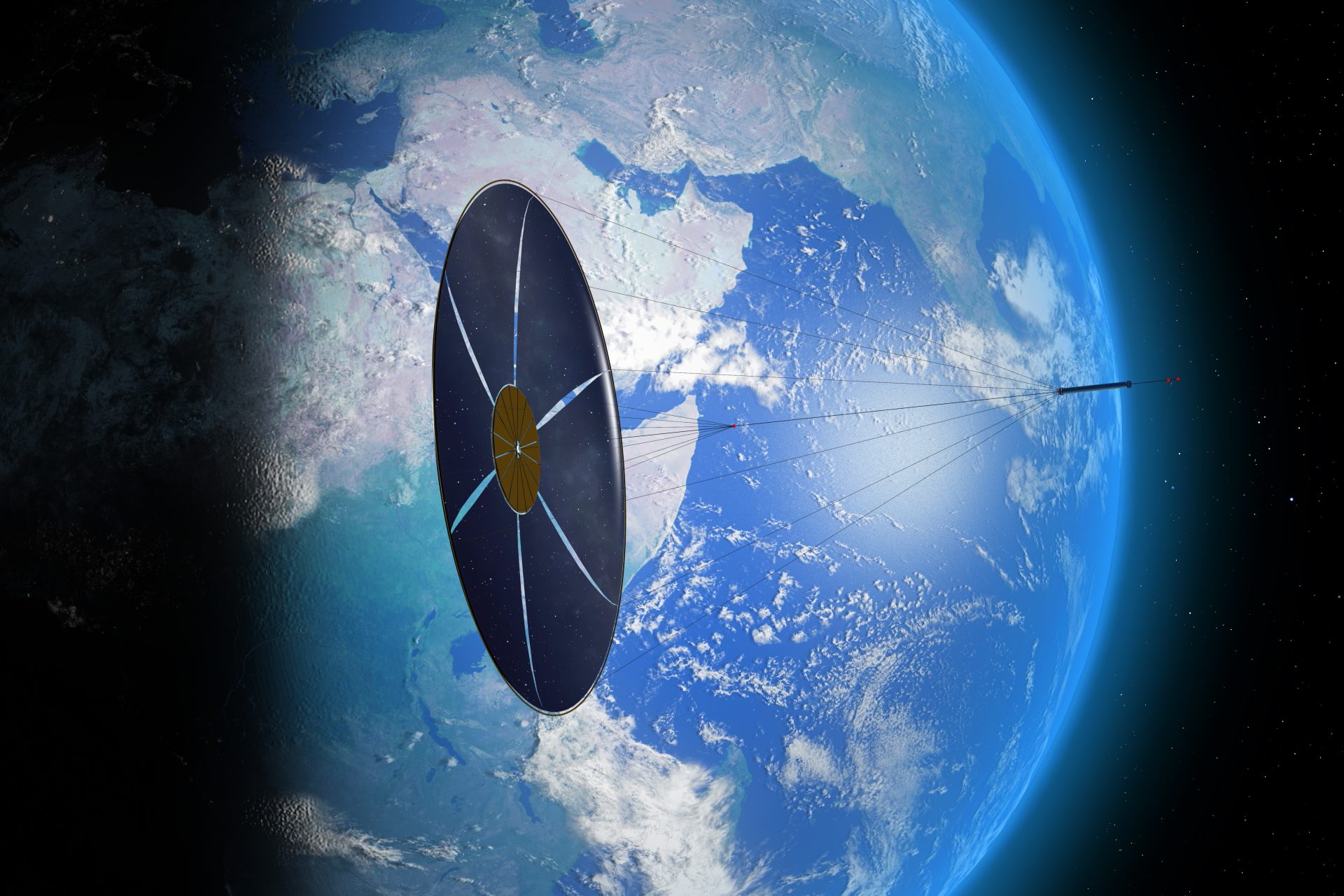
Obviously, solar sails will not be able to take humans to other planets quite yet, but the technology could be used for a wide variety of missions in space. But how exactly does a sail work in the vacuum of space (a place with no wind)?
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Andrzej Mirecki, Own Work, CC BY-SA 3.0
Solar sails aren’t exactly like the sails on a boat here on Earth but the concept is quite similar according to Space.com. Just like how wind can guide a sailboat, solar energy (photons) can be harnessed to help guide vessels through space.
“It only takes a slight amount of sunlight to guide solar sails through space,” Space.com noted, adding that although “photons don't have mass, they can force momentum when they hit an object,” which is how solar sails can move objects in space.
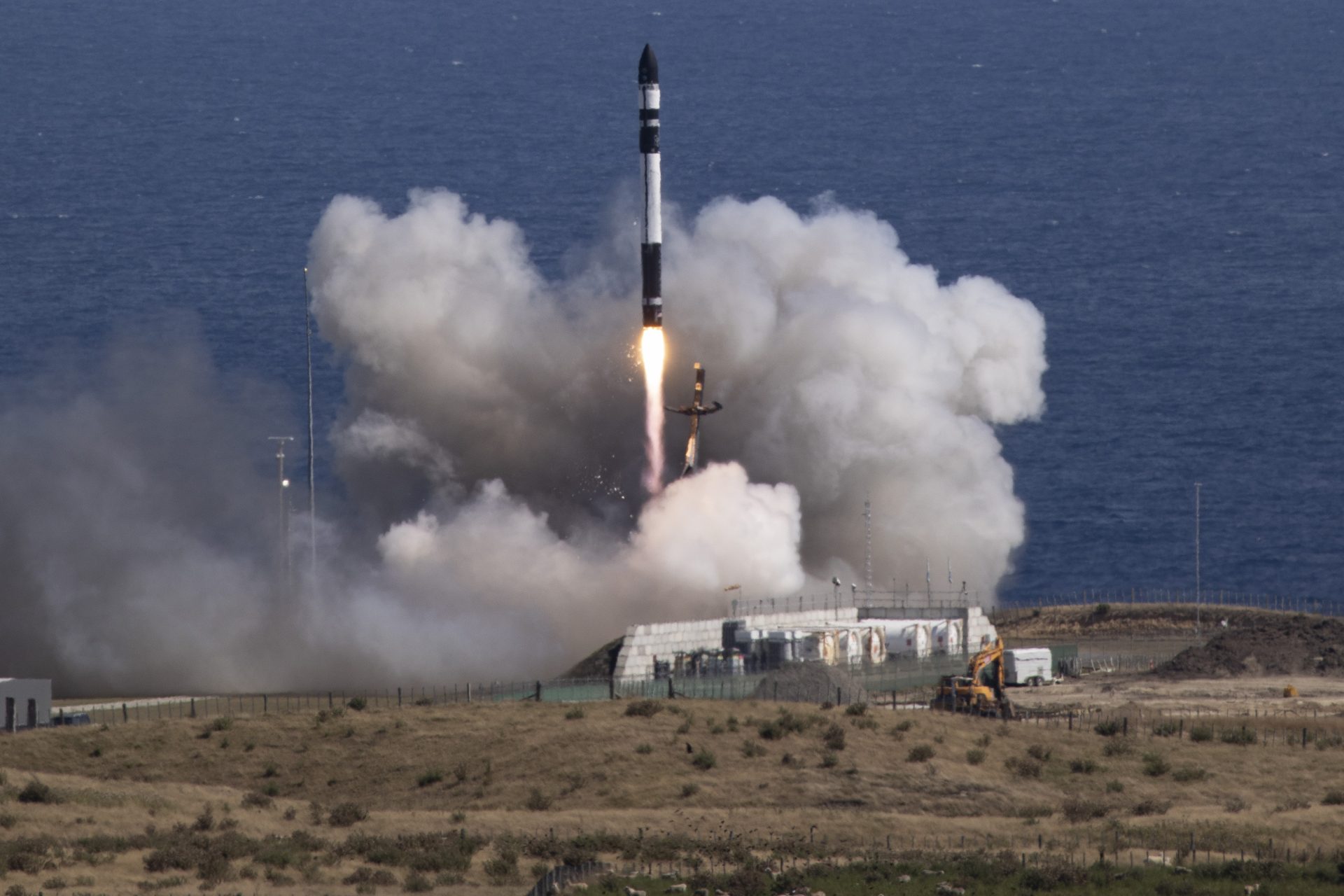
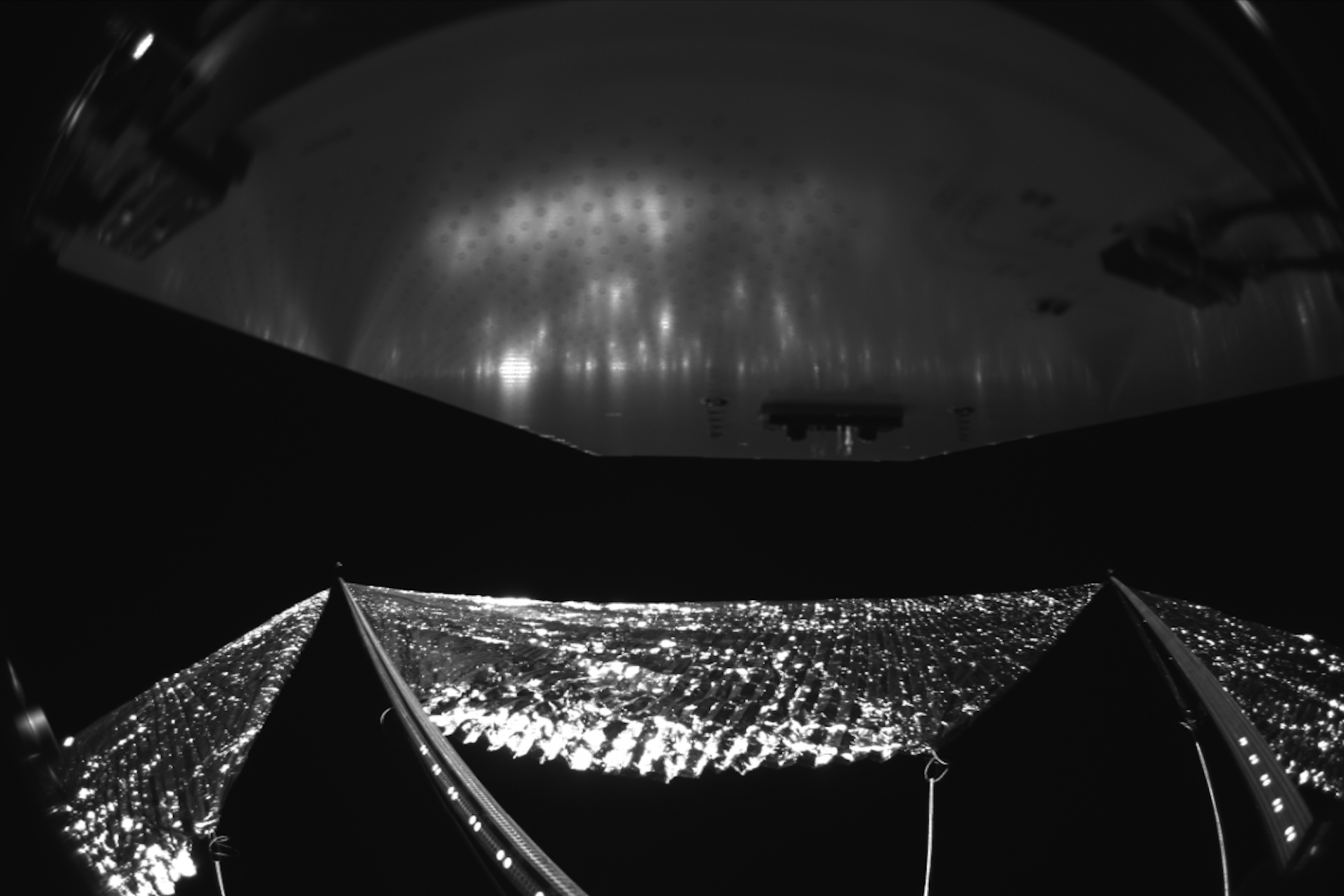
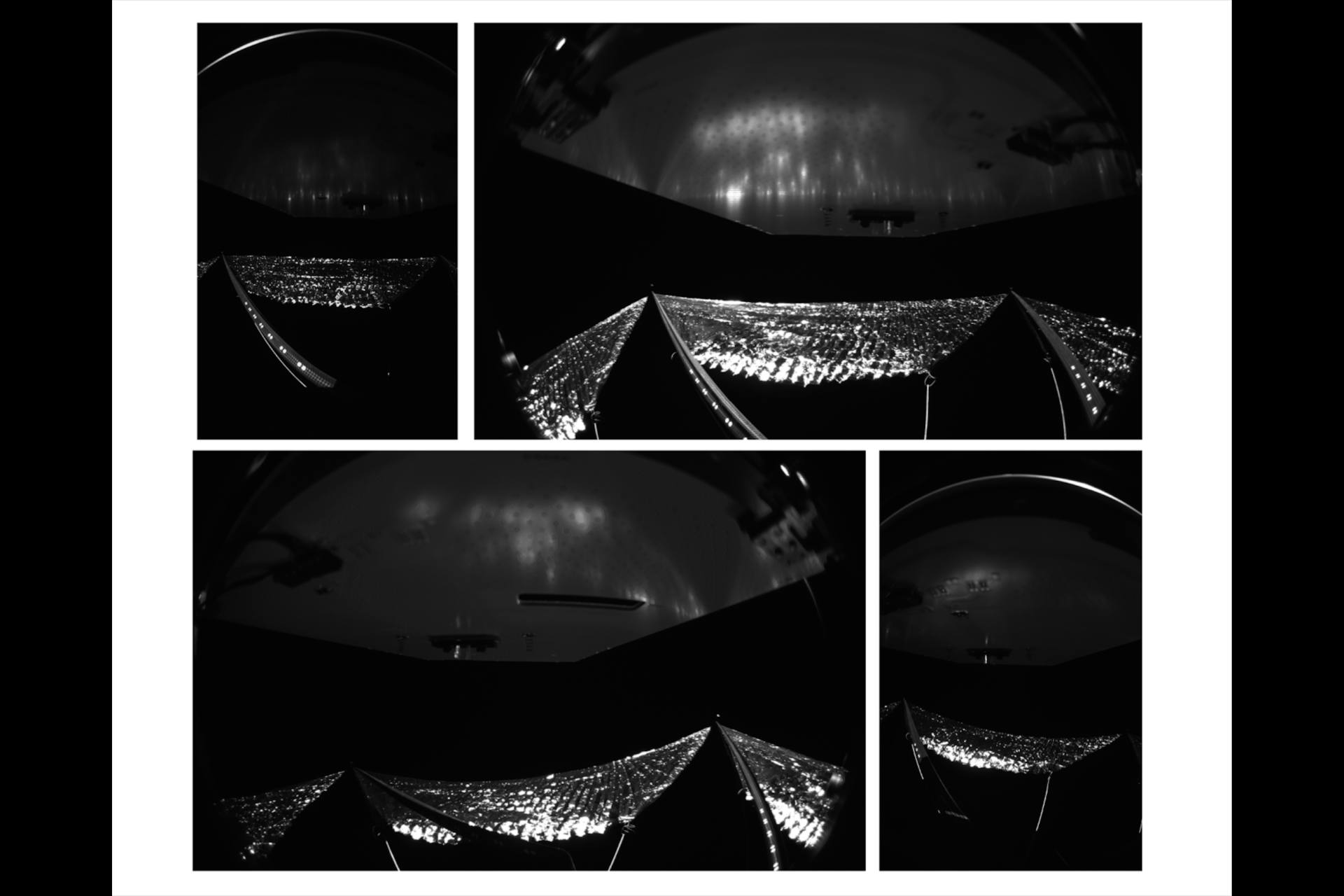
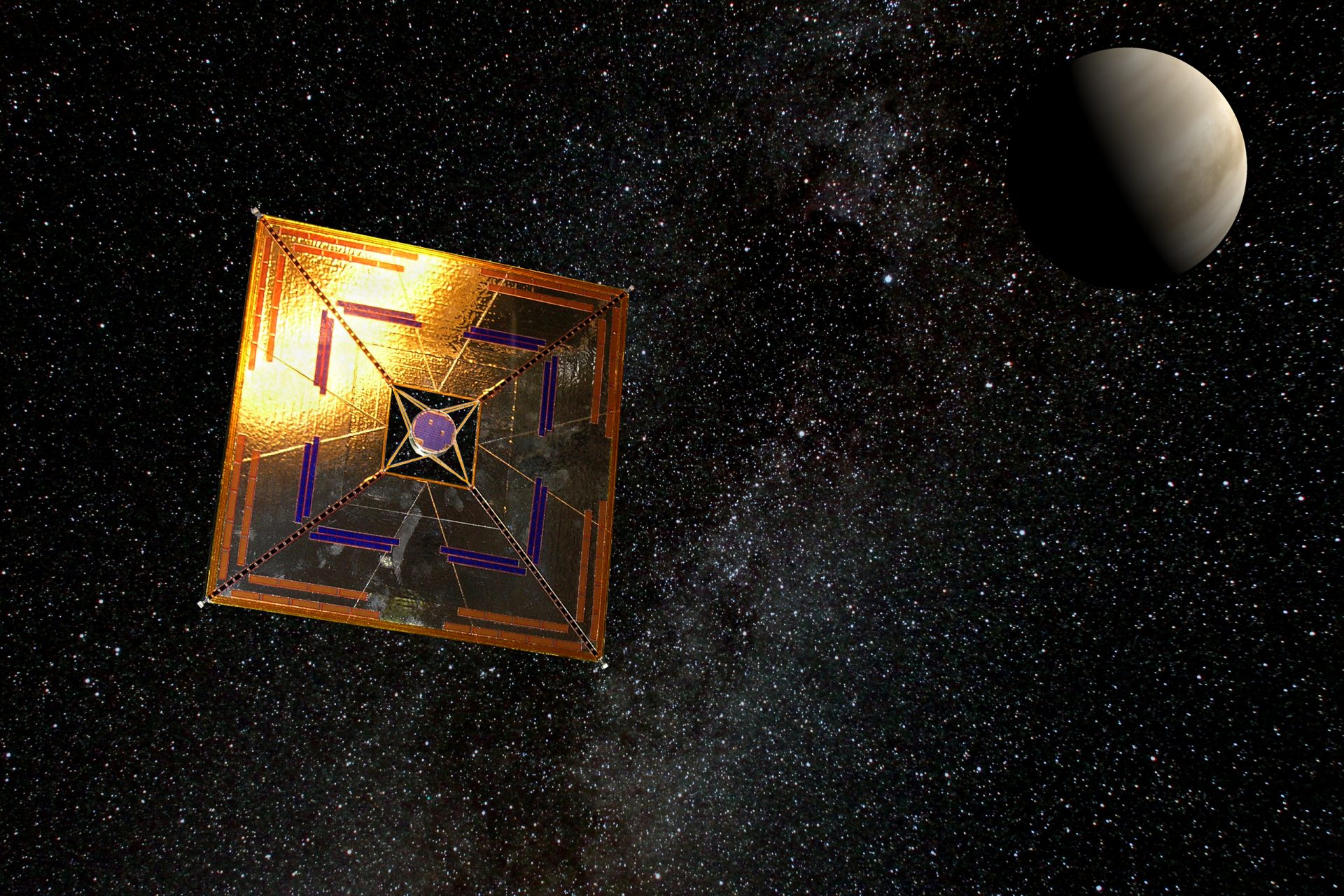
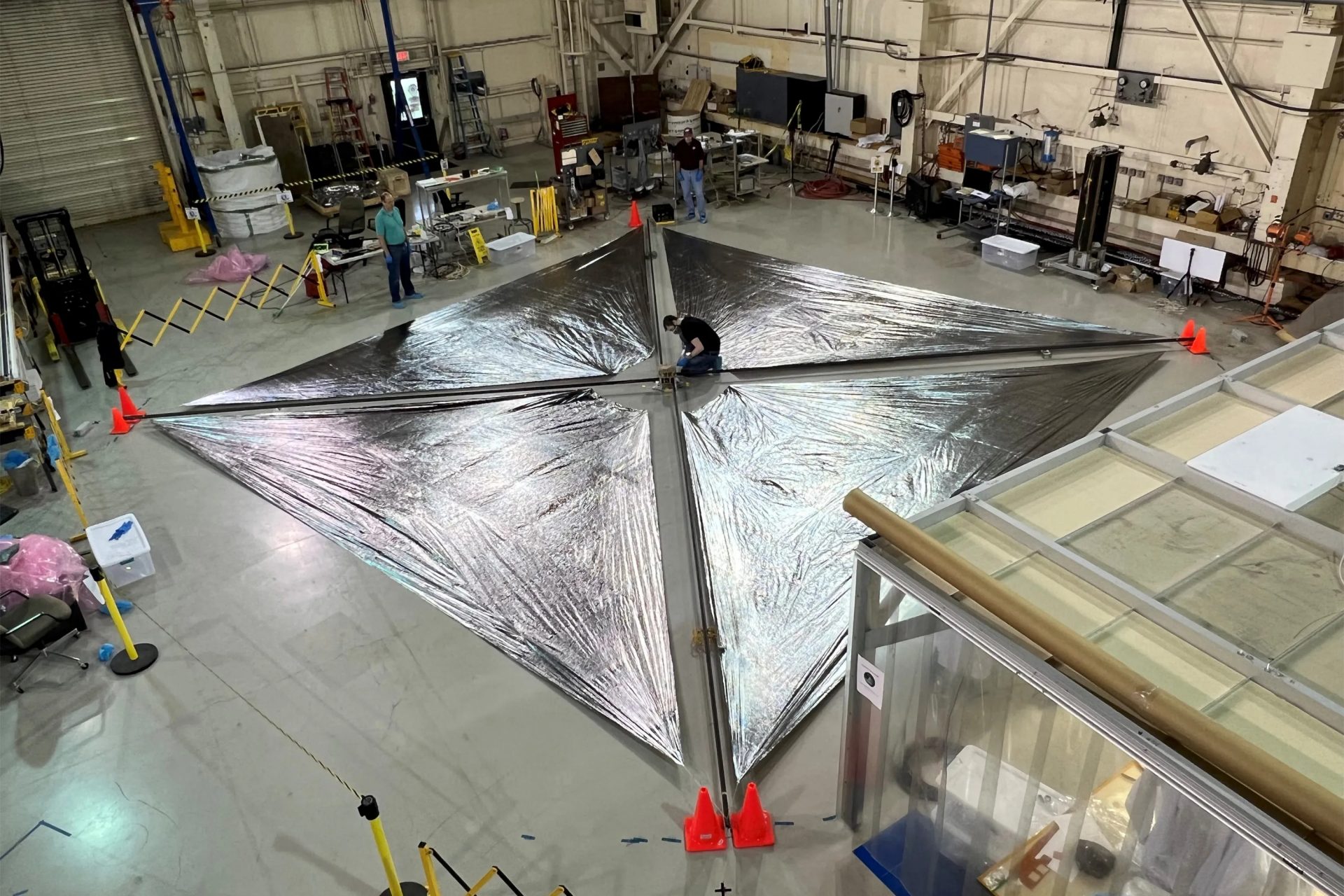
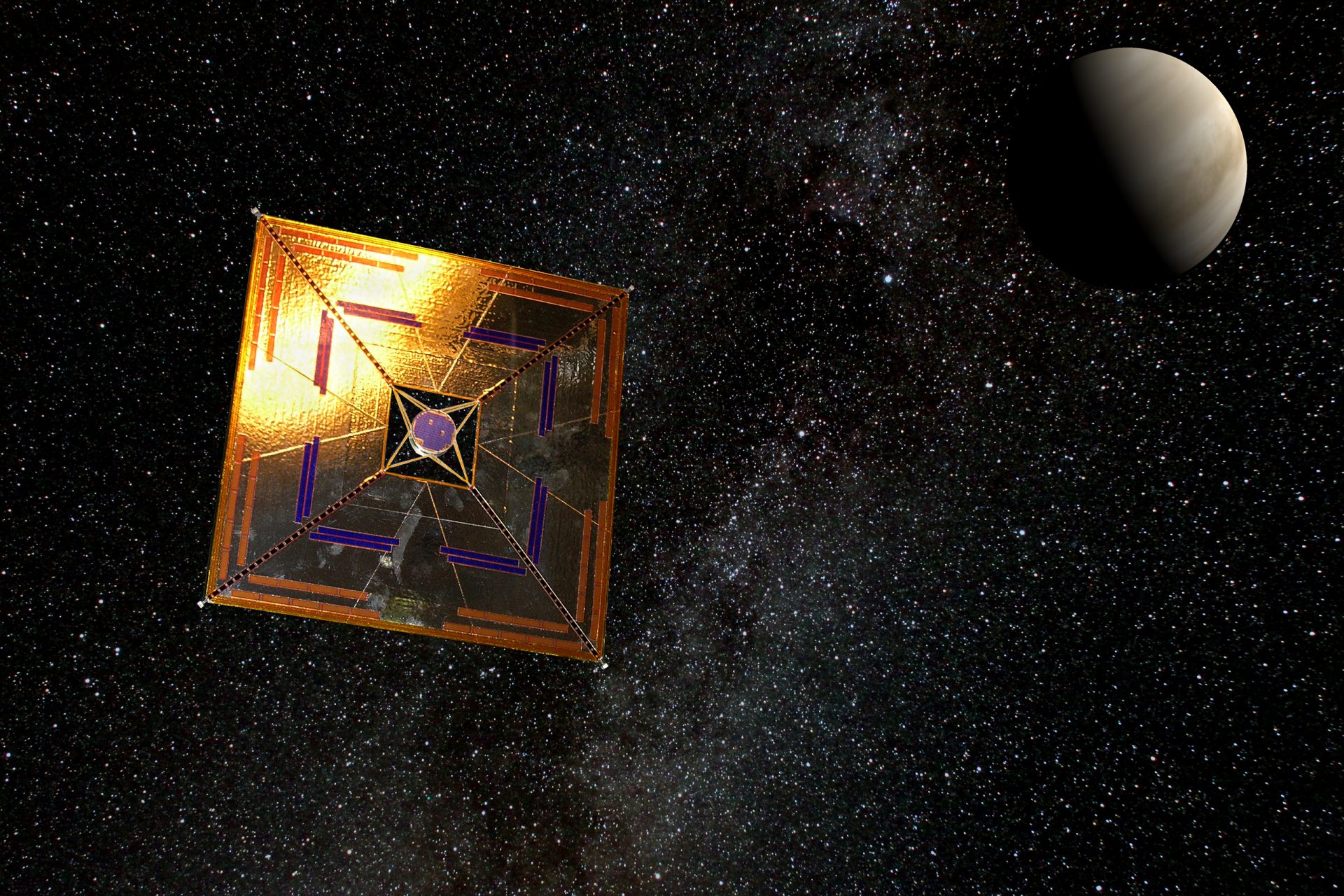
On April 24th, the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System (ACS3) headed up to space with Rocket Lab's Electron vehicle, and on August 29th, the ACS3 spread its solar sails in space for the first time, and it was captured by cameras fixed to its sails.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Scott Andrews, Public Domain
NASA published the first image from the ACS3’s sail deployment on September 5th, and it was a sight to see—even if its orientation was a bit confusing, something that NASA noted in its press release alongside the image.
Photo Credit: NASA
“The success so far of this mission is pretty awesome because solar sail technology is an incredibly impressive concept both in practice and in theory,” reported Live Science’s Monisha Ravisetti. But now the real work has begun for NASA's ACS3 team.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By NASA Ames Research Center / NASA/Aero Animation/Ben Schweighart
NASA’s new solar sail system was put to the test over the next proceeding weeks according to Space.com’s Meredith Garofalo, who reported that the maneuverability of the system was going to be observed so that more could be learned about how to improve the system in the future.
Photo Credit: NASA/Aero Animation/Ben Schweighart
"Raising and lowering the orbit of the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft will provide valuable information that may help guide future concepts of operations and designs for solar sail-equipped science and exploration missions,” NASA noted when in a press release about the ASC3 system.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By NASA, Public Domain
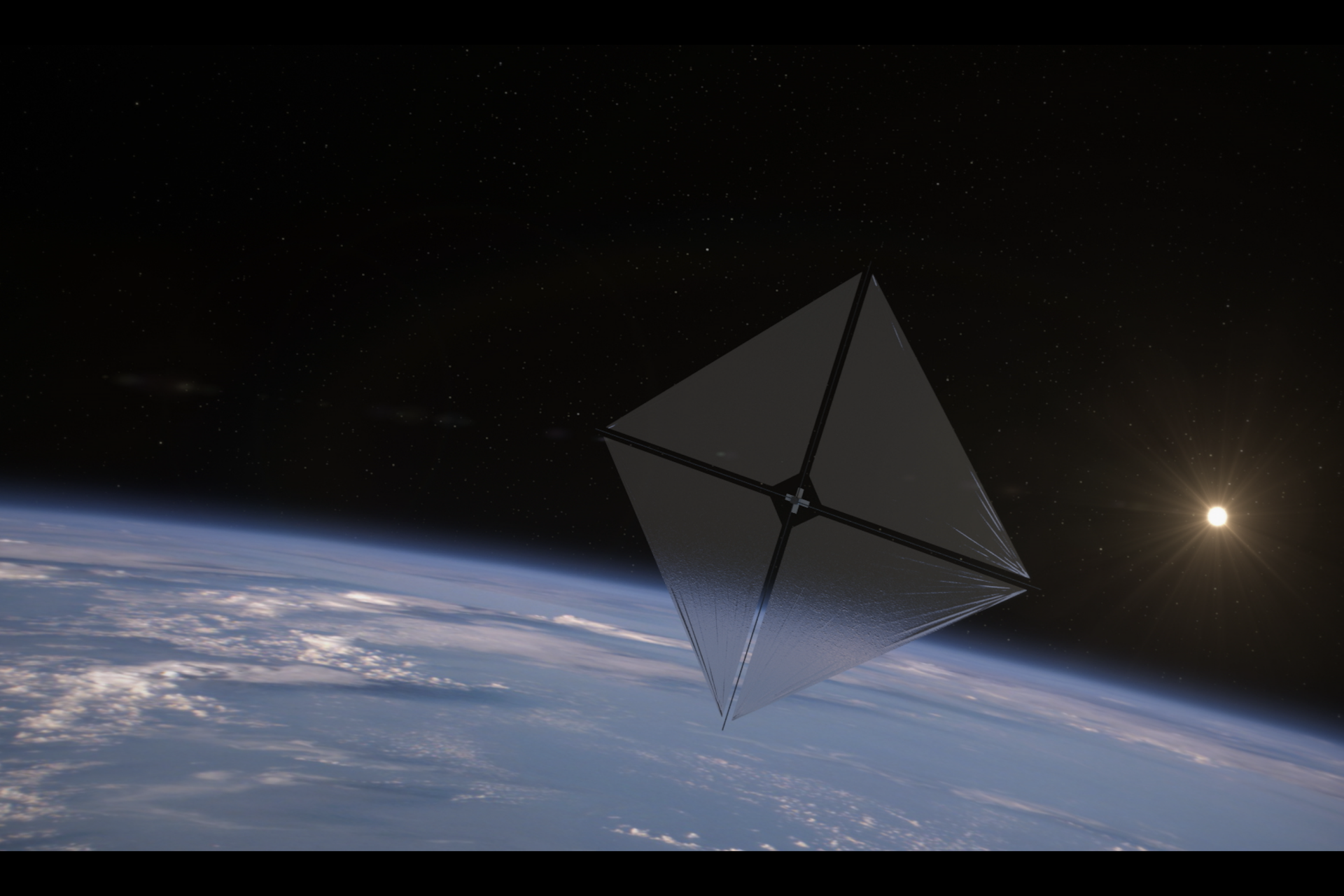
The ACS3 spacecraft orbits the Earth at nearly double the altitude of the International Space Station according to NASA, which also pointed out its sails span roughly 860 square feet or about 80 square meters (half the size of a tennis court for reference).
“Now, with the sail fully extended, the Solar Sail System may be visible to some keen skywatchers on Earth who look up at the right time,” a NASA press release noted.
Photo Credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls
Unfortunately, on October 22, NASA revealed that the boons of the solar system weren't in alignment and, more importantly, that one of them was likely bent, which presented a minor problem for the mission according to an official update.
"While the solar sail has fully extended to its square shape roughly half the size of a tennis court, the mission team is assessing what appears to be a slight bend in one of the four booms," the NASA update explained.
Photo Credit: NASA, Gianine Figliozzi
"This likely occurred as the booms and sail were pulled taut to the spacecraft during deployment," it adds. "Analysis indicates that the bend may have partially straightened over the weeks since boom deployment, while the spacecraft was slowly tumbling."
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By NASA Ames Research Center / Don Richey, Public Domain
As a result, the problematic boon caused the spacecraft to begin tumbling. However, the NASA update noted that the Solar Sail System's team didn't believe the bent boon would prohibit the ACS3 from being able to execute its sailing technology in later demonstrations.
Never miss a story! Click here to follow The Daily Digest.
Photo Credit: Wiki Commons By Andrzej Mirecki, Own Work, CC BY-SA 3.0
More for you
Top Stories